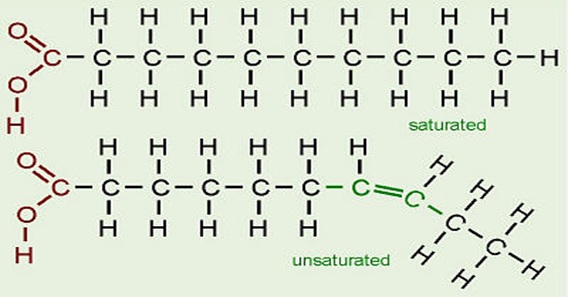
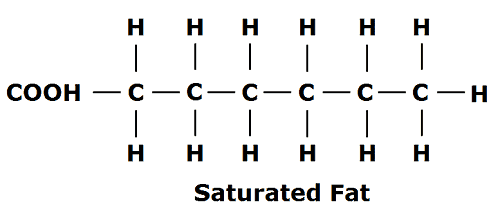
Fats are classified into three main groups, which are: Saturated fat. These are fats that have single bonds between their molecules and are “saturated” with hydrogen molecules.
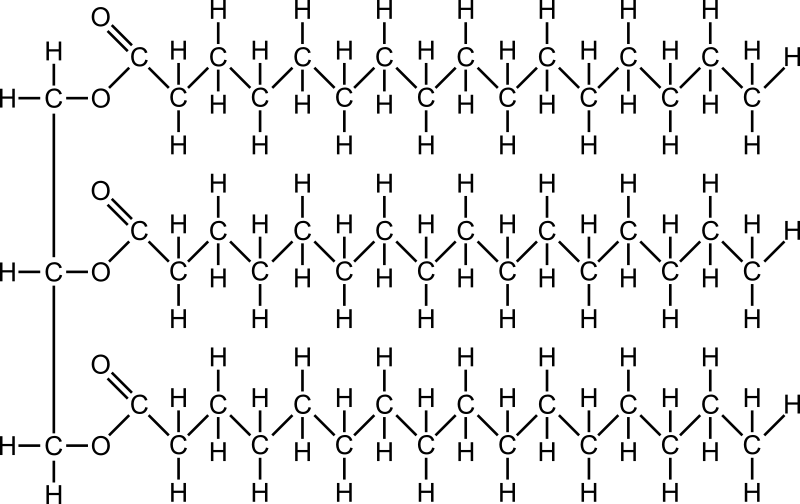
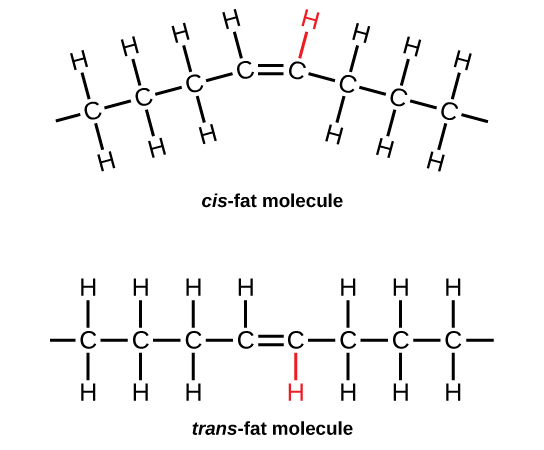
About Trans Fat . There are four kinds of fats: monounsaturated fat, polyunsaturated fat, saturated fat, and trans fat. Monounsaturated fat and polyunsaturated fat …
Health. Monounsaturated fats protect against cardiovascular disease by providing more membrane fluidity than saturated fats, but they are more vulnerable to …
To read more about heart disease and cholesterol, check out the special report page. It’s hard to overstate the impact that cardiovascular disease (CVD) has in the U.S..


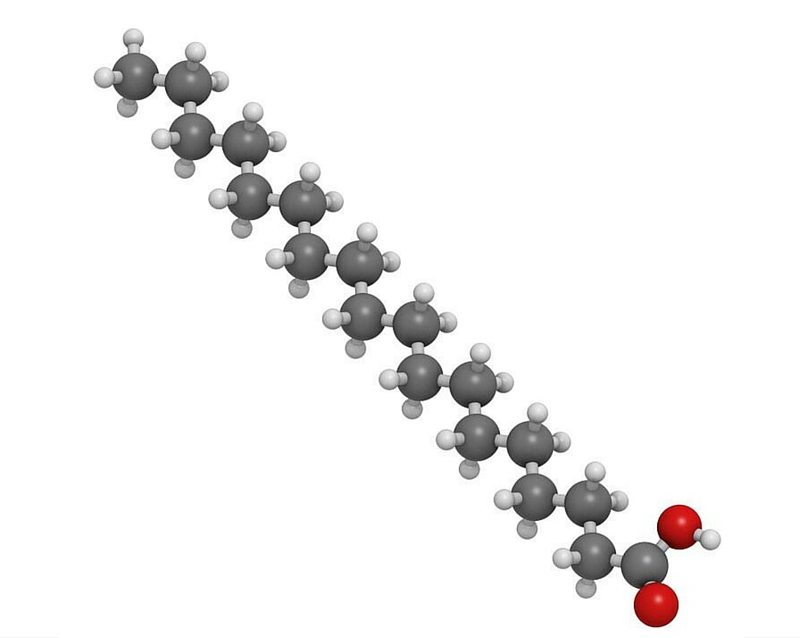
Eating foods that contain saturated fats raises the level of cholesterol in your blood. High levels of LDL cholesterol in your blood increase your risk of heart disease and stroke. From a chemical standpoint, saturated fats are simply fat molecules that have no double bonds between carbon molecules
Polyunsaturated fats can have a beneficial effect on your heart when eaten in moderation and when used to replace saturated fat and trans fat in your diet.

Despite having been demonized in the past, new studies have shown that saturated fat does not cause heart disease as previously believed.
A new meta-analysis pooling data from 21 studies and over 350,000 people found that there is no relationship between saturated fat intake and cardiovascular disease.
Saturated fat is one of the two main classes of fat, the other being unsaturated fat. These groups differ slightly in their chemical structure and properties.

