Reasons for testing. A glucose test may be recommended for a variety of reasons. One may be screening for gestational diabetes during pregnancy. This form of diabetes is temporary during pregnancy, and with glucose-controlling medication or insulin symptoms can be improved.
Find out how the oral glucose tolerance test can help diagnose diabetes. And see why anyone who is pregnant needs this test.


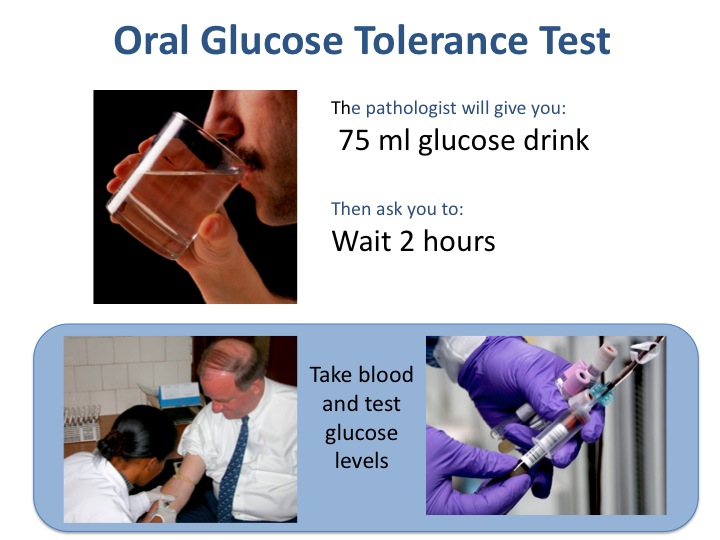

A glucose tolerance test measures how well your body is able to process glucose, or sugar. Your doctor can use it to diagnose diabetes.

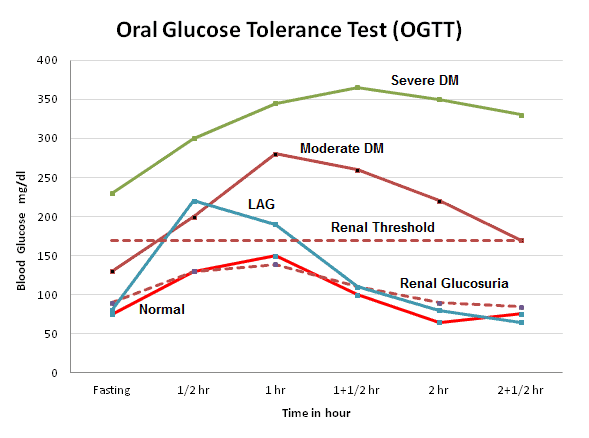
The oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) is currently the gold standard for the diagnosis of diabetes. The recommended preparation for and administration of the OGTT are important to ensure that test results are not affected. Interpretation is based on venous plasma glucose results before and 2 hours
Administer drink regardless of fasting glucose IF ‘Give glucose drink regardless of fasting glucose’ is written on the requisition. Clinicians may do this for certain patients, e.g. mother at high risk of GDM or early in pregnancy (< 20 weeks gestation).



Specimen* Plasma or Serum Glucose Level (Carpenter and Coustan Conversion) Plasma Glucose Level (National Diabetes Data Group Conversion) *The diagnosis of GDM can be made based on the result of the 100-gram, three-hour oral glucose tolerance test, for which there is evidence that treatment improves outcome.
Why it’s done. The glucose tolerance test identifies abnormalities in the way your body handles glucose after a meal — often before your fasting blood glucose …

The most common glucose tolerance test is the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). Before the test begins, a sample of blood will be taken. You will then be asked to drink a liquid containing a certain amount of glucose (usually 75 grams). Your blood will be taken again every 30 to 60 minutes after
Describes how glucose tests are used, when glucose tests are ordered, and what the results of a glucose test might mean
